If you’re interested in learning about the anatomy of the human body, you may be curious about the abdominal muscles. The abdominal muscles are a group of muscles that are located in the abdomen, which is the area between the chest and pelvis. These muscles play an important role in the movement of the body and the protection of the internal organs.
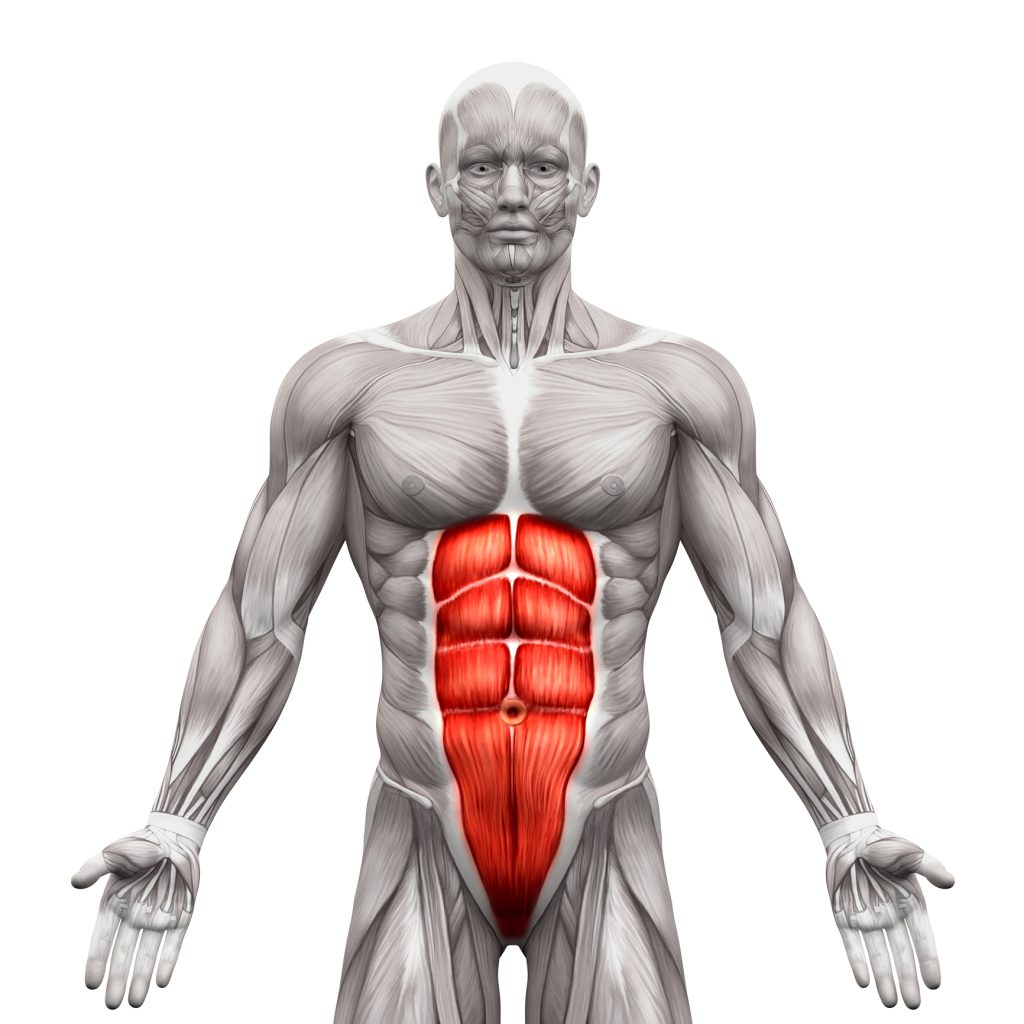
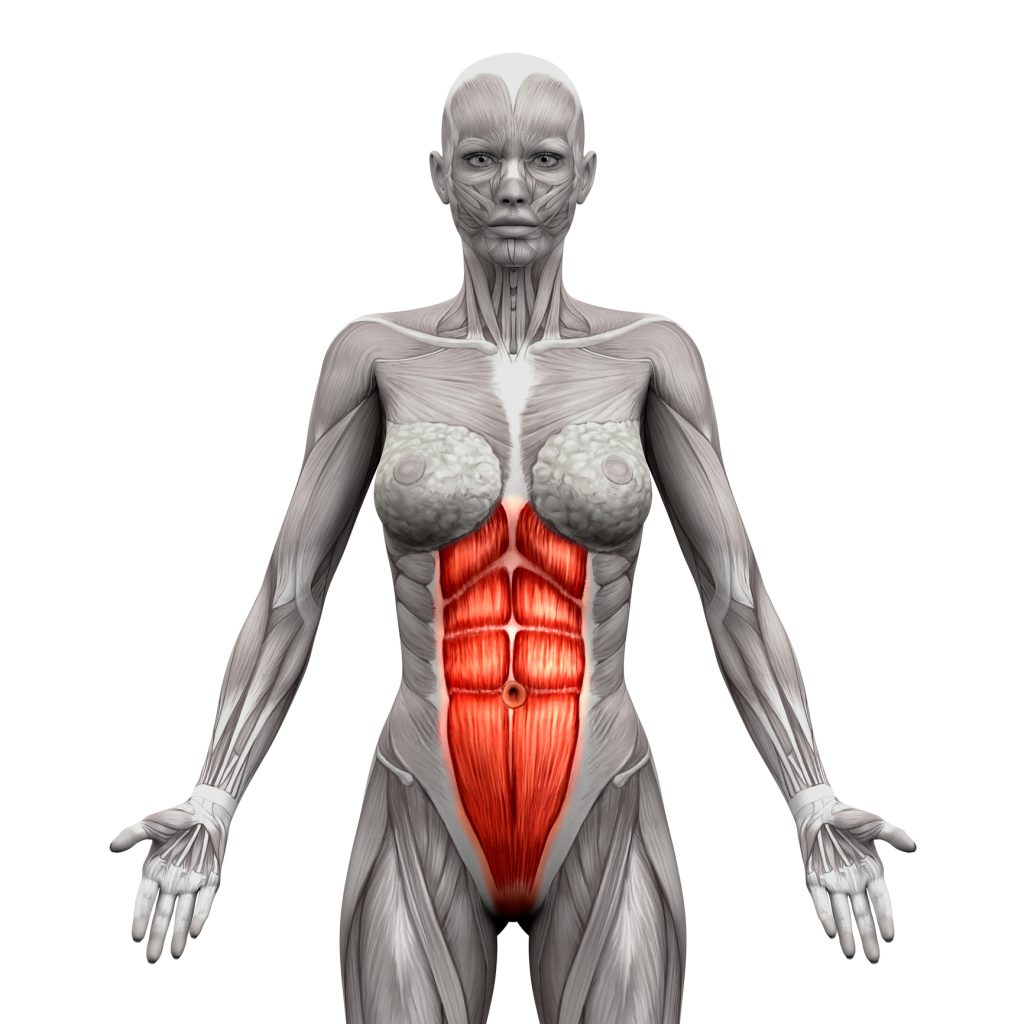
There are four main abdominal muscles: the rectus abdominis, the external obliques, the internal obliques, and the transverse abdominis. The rectus abdominis is the muscle that is commonly referred to as the “six-pack.” It runs vertically down the front of the abdomen and is responsible for flexing the trunk.
The external obliques are located on the sides of the abdomen and are responsible for rotating the trunk and bending it to the side. The internal obliques are located beneath the external obliques and are responsible for the same movements. Finally, the transverse abdominis is located deep within the abdomen and is responsible for stabilizing the trunk and compressing the internal organs.
Understanding Abdominal Muscles
When it comes to building a strong core, understanding the different muscles that make up the abdominal wall is crucial. The abdominal muscles are a group of four muscles that work together to support the spine and pelvis, aid in breathing, and help with the movement of the trunk. These muscles include the rectus abdominis, internal oblique, external oblique, and transversus abdominis.
The rectus abdominis is the most well-known of the abdominal muscles. It is a long, flat muscle that runs vertically down the front of the abdomen. This muscle is responsible for flexing the trunk, which means bringing the ribcage closer to the pelvis. It also plays a role in stabilizing the pelvis during movements like walking or running.
The internal oblique muscle is located on the sides of the abdomen, just beneath the external oblique. This muscle runs at a 90-degree angle to the external oblique and helps with the rotation of the trunk. It also helps to compress the abdomen, which can increase intra-abdominal pressure and provide support to the spine during heavy lifting.
The external oblique muscle is located on the sides of the abdomen, just above the internal oblique. This muscle runs diagonally across the abdomen and helps with the rotation of the trunk. It also plays a role in flexing the trunk and compressing the abdomen.
The transversus abdominis is the deepest of the abdominal muscles. It runs horizontally across the abdomen and helps to stabilize the spine and pelvis. This muscle is also important for breathing, as it helps to increase intra-abdominal pressure and support the diaphragm.
In summary, the abdominal muscles are a group of four muscles that work together to support the spine and pelvis, aid in breathing, and help with the movement of the trunk. Understanding the role of each muscle is important for building a strong core and preventing injury.
Role of Abdominal Muscles in Movement
When it comes to movement, the abdominal muscles play a crucial role in providing stability and support to the spine and trunk. These muscles work in conjunction with other muscles in the body to create movement and maintain balance.
One of the main functions of the abdominal muscles is to assist in the flexion of the trunk. This movement is essential in activities such as sit-ups, crunches, and bending over to pick up objects. The rectus abdominis muscle, also known as the “six-pack,” is the primary muscle responsible for trunk flexion.
In addition to trunk flexion, the abdominal muscles also play a vital role in maintaining balance during movement. The transverse abdominis muscle, located deep in the abdomen, helps to stabilize the spine and pelvis during activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
During movement, the internal and external oblique muscles work together to provide rotational stability. These muscles are responsible for twisting movements such as swinging a golf club or throwing a ball.
Finally, the rectus abdominis and the external oblique muscles work together to provide stability during lateral flexion of the trunk. This movement is essential in activities such as side bends and lateral movements in sports such as basketball and soccer.
In summary, the abdominal muscles play a vital role in movement, providing stability and support to the spine and trunk. Whether you are performing a sit-up, running, or playing a sport, these muscles work together with other muscles in the body to create movement and maintain balance.
Abdominal Muscles and Posture
Good posture is essential for a healthy body and a confident appearance. The abdominal muscles play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture. They provide stability to the pelvis and spine, which helps to maintain an erect posture.
There are four main abdominal muscles that work together to provide stability and support to the pelvis and spine. These muscles are the rectus abdominis, external obliques, internal obliques, and transversus abdominis.
The rectus abdominis is the muscle that forms the “six-pack” abs. It runs vertically from the pubic bone to the sternum and is responsible for flexing the trunk. The external obliques are located on the sides of the rectus abdominis and are responsible for rotating the trunk. The internal obliques are located beneath the external obliques and are responsible for rotating the trunk in the opposite direction. The transversus abdominis is located beneath the internal obliques and provides stability to the spine and pelvis.
Weak abdominal muscles can lead to poor posture, which can cause back pain and other problems. Strengthening the abdominal muscles can help to improve posture and reduce the risk of back pain.
In addition to strengthening the abdominal muscles, it is also important to maintain an erect posture throughout the day. This can be achieved by sitting up straight, standing tall, and avoiding slouching.
Overall, the abdominal muscles play a critical role in maintaining proper posture and stability. By strengthening these muscles and maintaining an erect posture, you can improve your overall health and well-being.
Influence on Breathing
Your abdominal muscles play an important role in breathing. The diaphragm is the primary respiratory muscle, but the abdominal muscles also contribute to breathing by controlling intra-abdominal pressure.
When you inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward, creating a vacuum in your chest that draws air into your lungs. At the same time, your abdominal muscles contract to increase intra-abdominal pressure, which helps to stabilize your spine and push the diaphragm down. This allows your lungs to expand fully and take in more air.
During exhalation, your diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, pushing air out of your lungs. Your abdominal muscles also relax, allowing intra-abdominal pressure to decrease. This helps to reduce the workload on your diaphragm and allows it to return to its resting position.
Research has shown that specific abdominal muscles are involved in postural tasks and are affected by respiratory maneuvers. For example, the timing of the onset of contraction in a brief postural task is influenced by respiratory activation of the abdominal muscles.
It is important to note that the abdominal muscles have other functions beyond their respiratory role. Studies have shown that they are involved in activities such as trunk stability, spinal movement, and posture control.
In summary, your abdominal muscles play an important role in breathing by controlling intra-abdominal pressure and helping to stabilize your spine. They are also involved in other activities beyond their respiratory role.
Exercises for Abdominal Muscles
When it comes to working out your abs, there are a variety of exercises that you can do to target the four main abdominal muscles: the rectus abdominis, the external obliques, the internal obliques, and the transversus abdominis. Incorporating a mix of exercises that target each of these muscles can help you build a strong core and achieve a toned midsection.
Abdominal Exercises
Some of the most popular exercises for working your abs include:
- Crunches: This classic exercise targets the rectus abdominis, the muscle that runs vertically down the front of your abdomen. To do a crunch, lie on your back with your knees bent and your hands behind your head. Lift your shoulders off the ground, engaging your abs as you do so, then lower back down.
- Russian twists: Russian twists target the external obliques, the muscles on the sides of your abdomen. To do a Russian twist, sit on the ground with your knees bent and your feet flat. Lean back slightly and lift your feet off the ground, then twist your torso to the left and touch your hands to the ground. Twist to the right and touch your hands to the ground on the other side.
- Planks: Planks are a great exercise for targeting the transversus abdominis, the deepest of the four abdominal muscles. To do a plank, get into a push-up position, then lower yourself down so that you’re resting on your forearms. Keep your body in a straight line from your head to your heels, engaging your abs to hold the position.
- Side planks: Side planks work the internal obliques, the muscles that run diagonally along the sides of your abdomen. To do a side plank, lie on your side with your legs straight and your feet stacked on top of each other. Prop yourself up on your forearm and lift your hips off the ground, forming a straight line from your head to your heels.
Core Training
In addition to these exercises, there are a variety of other core training workouts that can help you build a strong, toned midsection. Some popular options include:
- Pilates: Pilates is a form of exercise that focuses on building core strength and stability. Many Pilates exercises target the abdominal muscles, making it a great choice for anyone looking to tone their midsection.
- Yoga: Yoga is another great option for core training, as many yoga poses require you to engage your abs to maintain balance and stability.
Routine
When creating a workout routine for your abs, it’s important to incorporate a mix of exercises that target each of the four main abdominal muscles. Aim to do three to four sets of each exercise, with 10 to 15 reps per set. You can also vary the exercises you do from workout to workout to keep your routine interesting and challenging.
Remember to always listen to your body and stop any exercise if you experience pain or discomfort. With consistent effort and a well-rounded workout routine, you can build a strong, toned midsection and achieve your fitness goals.
Abdominal Muscles and Core Stability
When it comes to core stability, the abdominal muscles play a crucial role. The four main abdominal muscles are the rectus abdominis, external obliques, internal obliques, and transverse abdominis. These muscles work together to stabilize the trunk and support the spine during movement.
The rectus abdominis is the most well-known abdominal muscle and is commonly referred to as the “six-pack.” This muscle runs vertically from the pubic bone to the sternum and is responsible for flexing the spine. The external and internal obliques are located on the sides of the rectus abdominis and are responsible for rotating and side-bending the spine. The transverse abdominis is the deepest of the abdominal muscles and is responsible for stabilizing the spine and pelvis.
Core muscles are important for maintaining posture, balance, and stability during movement. They also help to transfer force between the upper and lower body. The deep muscles of the core are particularly important for stabilizing the spine and pelvis during movement. These muscles include the transverse abdominis, multifidus, and pelvic floor muscles.
To improve core stability, it is important to strengthen all of the abdominal muscles, including the deep muscles. Exercises such as planks, bird dogs, and bridges can be effective for targeting the core muscles. It is also important to incorporate functional movements that require the core muscles to work together, such as squats and deadlifts.
In summary, the abdominal muscles play a crucial role in core stability. The four main abdominal muscles work together to stabilize the trunk and support the spine during movement. To improve core stability, it is important to strengthen all of the abdominal muscles, including the deep muscles, through a variety of exercises.
Abdominal Muscles and Back Pain
If you are experiencing back pain, it is possible that your abdominal muscles may be involved. The abdominal muscles play an important role in supporting the spine and maintaining good posture. Weak or imbalanced abdominal muscles can lead to poor posture, which can put extra strain on the lower back muscles and lead to pain.
Research has shown that changes in the recruitment of abdominal muscles can occur in people with low back pain. One study found that people with chronic low back pain had decreased activity in the deep abdominal muscle, transversus abdominis, compared to healthy individuals (Spine Journal). Another study found that people with chronic low back pain had decreased endurance in their abdominal muscles compared to healthy individuals (ScienceDirect).
One way to improve the function of the abdominal muscles and potentially reduce back pain is through targeted exercises. Core exercises that focus on the abdominal muscles have been shown to increase muscle thickness and improve disability in people with chronic low back pain (PubMed Central). Additionally, postural abdominal muscle endurance has been found to be associated with back pain incidence (ScienceDirect).
In summary, the abdominal muscles play an important role in supporting the spine and maintaining good posture. Weak or imbalanced abdominal muscles can lead to poor posture, which can put extra strain on the lower back muscles and lead to pain. Exercises that target the abdominal muscles may help improve their function and potentially reduce back pain.
Common Injuries and Prevention
When it comes to abdominal muscles, there are a few common injuries that you should be aware of. These injuries can range from overstretching to muscle strains, and they can be caused by overuse or sudden movements. Here are a few examples of common abdominal muscle injuries:
- Muscle strain: A muscle strain occurs when the muscle fibers are stretched or torn. This can happen when you overuse your abdominal muscles or perform sudden movements, such as twisting or lifting heavy objects.
- Overstretching: Overstretching your abdominal muscles can cause them to become weak and less flexible. This can make it more difficult to perform certain exercises and movements.
- Overuse: Overusing your abdominal muscles can lead to fatigue and weakness. This can make it more difficult to maintain proper form during exercises and can increase your risk of injury.
To prevent these injuries, it’s important to take care of your abdominal muscles. This includes stretching before and after exercise, taking breaks when needed, and avoiding sudden movements that can strain your muscles. Here are a few tips for preventing abdominal muscle injuries:
- Rest: Make sure to give your abdominal muscles time to rest and recover between workouts. This can help prevent overuse injuries and muscle strains.
- Stretching: Incorporate stretching into your exercise routine to improve flexibility and prevent overstretching injuries.
- Proper form: Use proper form when performing exercises that target your abdominal muscles. This can help prevent sudden movements that can strain your muscles.
- Abdominal strengthening: Incorporate exercises that strengthen your abdominal muscles, such as planks and crunches, into your workout routine. This can help prevent muscle strains and overuse injuries.
By taking care of your abdominal muscles and following these tips, you can help prevent common injuries and keep your core strong and healthy.
Role in Support and Protection
Your abdominal muscles play a crucial role in supporting and protecting your spine, as well as your internal organs. The four main abdominal muscles are the rectus abdominis, external obliques, internal obliques, and transverse abdominis.
The rectus abdominis muscle runs vertically from your pubic bone to your sternum and is responsible for flexing your trunk. The external and internal obliques are located on the sides of your abdomen and are responsible for rotating and bending your trunk. The transverse abdominis muscle is located deep within your abdomen and is responsible for stabilizing your spine.
One important structure that your abdominal muscles support is the linea alba, a fibrous band that runs down the center of your abdomen. This structure helps to distribute the forces generated by your abdominal muscles and provides a strong attachment point for your muscles.
In addition to supporting your spine and linea alba, your abdominal muscles also protect your internal organs and viscera. When you engage your abdominal muscles, you increase the pressure within your abdominal cavity, which helps to support and protect your organs. This increase in pressure also helps to prevent hernias and other abdominal injuries.
Overall, your abdominal muscles play a vital role in supporting and protecting your body. By engaging in exercises that target these muscles, you can improve your posture, reduce your risk of injury, and enhance your overall physical performance.
Diet and Lifestyle Impact
Your diet and lifestyle can have a significant impact on the development and strength of your abdominal muscles. Here are some ways your diet and lifestyle can affect your abdominal muscles:
Diet
Eating a healthy diet is crucial for developing and maintaining strong abdominal muscles. A diet that is high in protein, healthy fats, and fiber can help you build strong abdominal muscles. Here are some foods that can help:
- Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, and tofu
- Healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil
- Fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
On the other hand, a diet that is high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can weaken your abdominal muscles. These foods can cause inflammation in the body, which can lead to weakened muscles. Here are some foods to avoid:
- Processed foods such as chips, cookies, and crackers
- Sugary drinks such as soda and juice
- Unhealthy fats such as trans fats and saturated fats found in fried foods and fatty meats
Lifestyle
Your lifestyle can also impact the strength of your abdominal muscles. Here are some lifestyle factors to consider:
- Exercise: Regular exercise, including strength training and cardio, can help you build and maintain strong abdominal muscles. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
- Posture: Poor posture can weaken your abdominal muscles over time. Make sure to sit and stand up straight to engage your core muscles.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to inflammation in the body, which can weaken your abdominal muscles. Consider incorporating stress-reducing practices such as meditation or yoga into your routine.
- Sleep: Lack of sleep can also lead to inflammation in the body and weakened muscles. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to give your body time to repair and recover.
It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to develop a personalized plan to help you build and maintain strong abdominal muscles.
Abdominal Muscles in Daily Activities
Your abdominal muscles play an important role in many daily activities. These muscles provide support for your spine, pelvis, and internal organs. They also help you breathe, cough, sneeze, and defecate. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at how your abdominal muscles are involved in various daily activities.
Running
When you run, your abdominal muscles help stabilize your torso and prevent excessive movement. This helps you maintain proper form and reduces the risk of injury. The rectus abdominis muscle, which runs vertically down the front of your abdomen, is particularly important for running. It helps you maintain a stable pelvis and spine, which is essential for efficient running.
Coughing and Sneezing
Coughing and sneezing both involve the rapid expulsion of air from your lungs. This requires a strong contraction of your abdominal muscles to increase the pressure in your chest and push the air out. The transverse abdominis muscle, which wraps around your abdomen like a corset, is particularly important for coughing and sneezing. It helps you generate the necessary force to expel air from your lungs.
Defecating
Defecating involves the coordinated action of several muscles, including your abdominal muscles. When you bear down to have a bowel movement, your abdominal muscles contract to increase the pressure in your abdomen and help push the stool out. The external and internal oblique muscles, which run diagonally across your abdomen, are particularly important for defecating. They help you generate the necessary force to expel the stool.
Lifting
Lifting heavy objects requires a strong contraction of your abdominal muscles to stabilize your spine and prevent injury. The rectus abdominis and oblique muscles are particularly important for lifting. They help you maintain proper form and generate the necessary force to lift the object.
Walking
Walking involves a complex interplay of muscles, including your abdominal muscles. When you walk, your abdominal muscles help stabilize your pelvis and spine, which is essential for efficient walking. The transverse abdominis and rectus abdominis muscles are particularly important for walking. They help you maintain proper form and generate the necessary force to move forward.
In summary, your abdominal muscles are involved in many daily activities, including running, coughing, sneezing, defecating, lifting, and walking. These muscles provide support for your spine, pelvis, and internal organs, and help you breathe, cough, sneeze, and defecate. Understanding how your abdominal muscles work can help you improve your performance in these activities and reduce the risk of injury.
Anatomy of Abdominal Muscles
To understand the four main abdominal muscles, it’s important to have a basic understanding of the anatomy of the abdominal region. The abdominal muscles are a group of muscles that make up the front and side walls of the abdominal cavity. They are responsible for supporting the spine, protecting the internal organs, and aiding in breathing and movement.
The abdominal muscles are made up of several layers of muscle fibers that run in different directions. The outermost layer is called the external oblique, which runs diagonally from the ribs to the iliac crest and pubic crest. The internal oblique is the next layer, which runs perpendicular to the external oblique. The transverse abdominis is the deepest layer, which runs horizontally across the abdomen. The rectus abdominis is the most well-known muscle of the abdominal group, which runs vertically from the pubic bone to the sternum.
The abdominal muscles are connected to the pelvis and spine by a layer of connective tissue called fascia. The fascia helps to stabilize the muscles and allows them to work together to support the spine and pelvis. The iliac crest and inguinal ligament are also important landmarks in the anatomy of the abdominal muscles. The iliac crest is the curved ridge at the top of the hip bone, while the inguinal ligament is the band of tissue that runs from the pubic bone to the iliac crest.
In summary, the four main abdominal muscles are the external oblique, internal oblique, transverse abdominis, and rectus abdominis. These muscles work together to support the spine, protect the internal organs, and aid in breathing and movement. Understanding the anatomy of the abdominal muscles is important for anyone looking to improve their core strength and overall fitness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the anatomy of the abdominal muscles is crucial for anyone looking to improve their core strength or undergo abdominal surgery. The four main abdominal muscles are the rectus abdominis, external obliques, internal obliques, and transverse abdominis.
Each of these muscles plays a unique role in supporting the spine, stabilizing the pelvis, and flexing or rotating the trunk. By working all four muscles in a balanced way, you can achieve a strong and stable core that can help improve your posture, prevent injury, and enhance athletic performance.
It’s important to note that while exercises like crunches and sit-ups can target the rectus abdominis, they may not engage the other three muscles as effectively. Incorporating exercises that target all four muscles, such as planks, side planks, and bird dogs, can help ensure that you’re working your entire core.
Overall, understanding the anatomy and function of the abdominal muscles can help you achieve a strong and stable core, which can have numerous benefits for your overall health and well-being. With the right exercises and proper form, you can build a strong and functional core that supports your body in all of your daily activities.






Leave a Reply