Abdominal strain refers to the tearing or stretching of the muscles in the abdominal region. This type of injury commonly occurs during physical activities that involve twisting, bending, or sudden movements. The diagnosis of an abdominal strain typically involves a thorough physical examination and may require additional imaging tests such as an ultrasound or MRI. The treatment for an abdominal strain focuses on relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and promoting healing.
To diagnose an abdominal strain, a healthcare professional will typically ask about the patient’s symptoms and medical history, followed by a physical examination. During the examination, the healthcare provider may palpate the abdominal area to identify areas of tenderness or swelling. They may also assess the range of motion in the affected area and check for any muscle spasms. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be recommended to obtain a more detailed view of the injured muscles.
Treatment for an abdominal strain usually involves a combination of rest, pain management, and physical therapy. Resting the injured area is crucial to allow the muscles to heal. Applying ice packs to the abdomen can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. Physical therapy exercises, such as gentle stretching and strengthening exercises, may be recommended to gradually restore the flexibility and strength of the abdominal muscles.
In conclusion, the diagnosis of an abdominal strain involves a physical examination and may require additional imaging tests. The treatment for this type of injury focuses on rest, pain management, and physical therapy exercises. It is important for students to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for abdominal strain to prevent and manage this common injury effectively.
Diagnosing Abdominal Strain
Diagnosing abdominal strain involves a thorough examination and evaluation of the patient’s symptoms and medical history. The first step in diagnosing this condition is to perform a physical examination. During this examination, the healthcare provider will palpate the abdomen to check for areas of tenderness or swelling. They may also ask the patient to perform certain movements or exercises to assess their range of motion and identify any areas of pain or discomfort.
In addition to the physical examination, the healthcare provider may order diagnostic tests such as X-rays or ultrasound to get a more detailed view of the abdominal area. These tests can help rule out other potential causes of the symptoms and confirm the diagnosis of an abdominal strain.
Once the diagnosis of abdominal strain is confirmed, the healthcare provider will develop a treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs. The primary goal of treatment is to relieve pain and promote healing. Initially, the healthcare provider may recommend rest and avoiding activities that aggravate the pain.
They may also suggest applying ice packs to the affected area to reduce inflammation and swelling. Depending on the severity of the strain, the healthcare provider may prescribe pain medication or anti-inflammatory drugs to help manage the symptoms. Physical therapy may also be recommended to help strengthen the abdominal muscles and prevent future strains.
In some cases, more invasive treatments may be necessary for severe or chronic abdominal strain. These may include corticosteroid injections into the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain, or in rare cases, surgery may be required to repair any torn or damaged abdominal muscles.
However, these interventions are typically reserved for cases where conservative treatments have failed to provide adequate relief. Overall, the prognosis for abdominal strain is generally good, and most patients are able to recover fully with appropriate treatment and rehabilitation.
Imaging techniques
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal strain. When a patient presents with symptoms of an abdominal strain, imaging techniques are used to accurately identify the extent and location of the injury. One of the most commonly used imaging techniques for abdominal strain is an X-ray. X-rays provide a clear image of the bones and can help identify any fractures or dislocations that may be present. However, X-rays are limited in their ability to visualize soft tissues, making them less effective in diagnosing abdominal strain.
Another imaging technique that is commonly used for diagnosing abdominal strain is ultrasound. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and soft tissues. It is a non-invasive procedure and does not expose the patient to any radiation. Ultrasound can provide valuable information about the condition of the abdominal muscles, tendons, and ligaments. It can also help identify any fluid accumulation or swelling in the abdomen.
In some cases, more advanced imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be required to diagnose and treat abdominal strain. MRI uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to generate detailed images of the soft tissues in the abdomen.
It provides a more comprehensive view of the injury, allowing healthcare professionals to accurately assess the extent of the abdominal strain. CT scans, on the other hand, use X-rays and computer technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the abdomen. This imaging technique is particularly useful in identifying any internal bleeding or damage to the organs.
In conclusion, imaging techniques are essential in the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal strain. X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans are commonly used to accurately identify and assess the extent of the injury.
These imaging techniques provide valuable information that guides healthcare professionals in developing an appropriate treatment plan, whether it involves conservative measures or surgical intervention. By utilizing these imaging techniques, healthcare professionals can effectively diagnose and treat abdominal strain, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Physical examinations
Physical examinations are an essential component of diagnosing and treating abdominal strains. When a patient presents with symptoms such as pain or discomfort in the abdominal region, a thorough physical examination is conducted to assess the extent and location of the injury. The examination typically begins with the patient’s medical history being reviewed, including any previous abdominal injuries or surgeries. This helps the healthcare provider evaluate the potential causes and severity of the strain.
During the physical examination, the healthcare provider will palpate the abdomen to identify areas of tenderness, swelling, or muscle spasms. They may also ask the patient to perform certain movements or exercises to assess their range of motion and identify any specific activities that exacerbate the pain. In some cases, additional tests, such as X-rays or ultrasound, may be ordered to rule out other potential causes of abdominal pain.
Once the physical examination is completed, the healthcare provider can make a more accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment plan for the abdominal strain. This may include a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as over-the-counter pain medications to manage discomfort.
In more severe cases, physical therapy or referral to a specialist may be necessary. The physical examination is crucial in guiding the treatment approach, as it allows the healthcare provider to understand the specific nature of the abdominal strain and tailor interventions accordingly.
Treating Abdominal Strain
Abdominal strain refers to the tearing or stretching of the muscles in the abdominal region. This type of injury often occurs during physical activities that involve sudden movements, such as sports or heavy lifting. When it comes to treating abdominal strain, there are various methods that can be effective in relieving pain and promoting the healing process.
One of the most commonly recommended treatments for abdominal strain is rest. By avoiding any activities that may further strain the muscles, individuals can give their bodies the time and opportunity to heal naturally. This may involve refraining from participating in sports or engaging in any strenuous physical activities. Resting also helps in reducing inflammation and preventing further damage to the affected muscles.
In addition to rest, applying ice to the injured area can also be beneficial. Cold therapy helps in reducing swelling and numbing pain. Individuals can use an ice pack or even a bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a towel and apply it to the abdomen for around 15-20 minutes every few hours. However, it is important to avoid applying ice directly to the skin to prevent ice burns.
Another effective treatment for an abdominal strain is the use of over-the-counter pain medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help in reducing pain and inflammation. It is important to follow the recommended dosage instructions and consult a healthcare professional before taking any medication, especially if there are any underlying medical conditions or allergies.
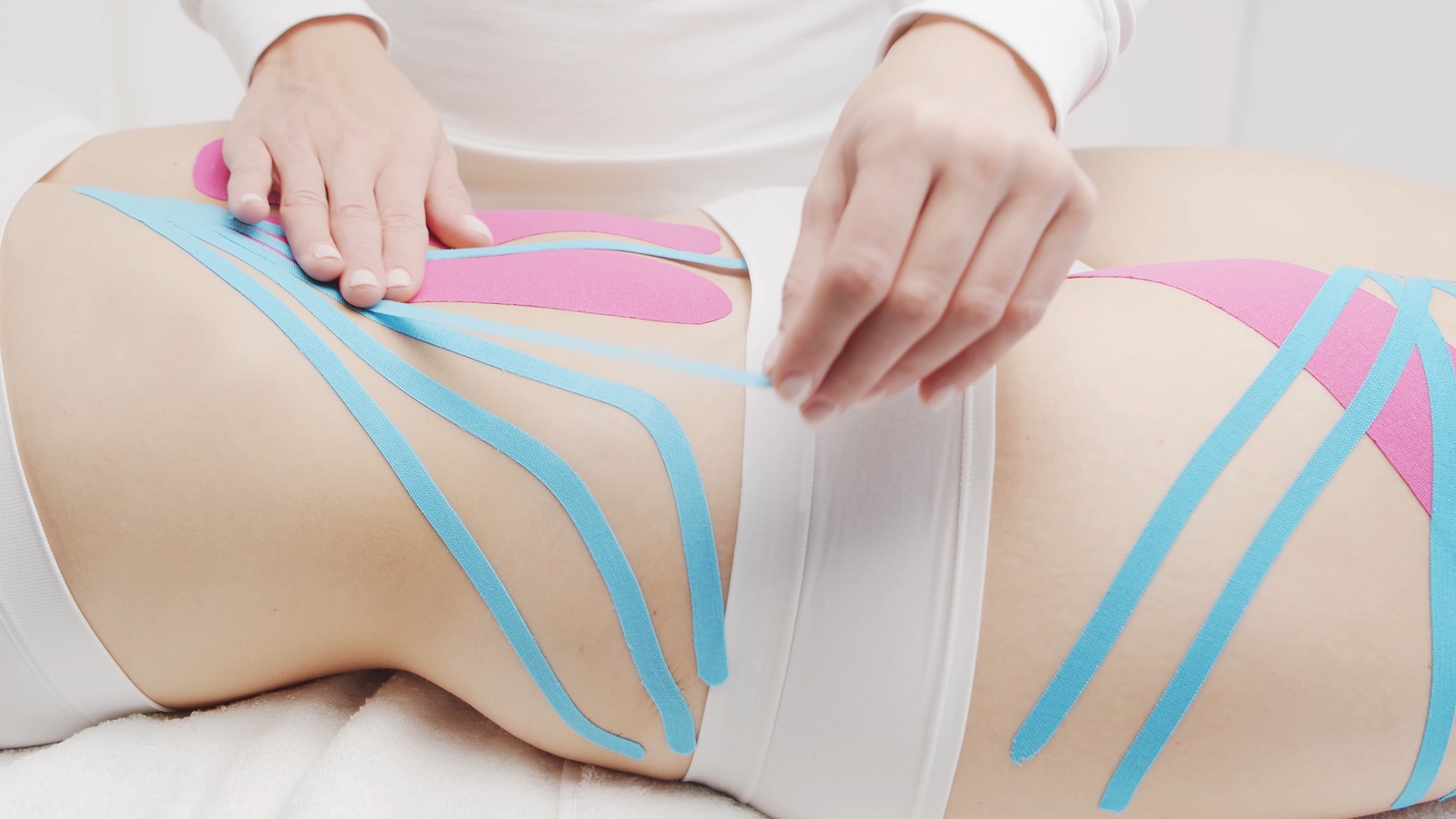
Incorporating elastic tape as part of the recovery treatment for abdominal strains can significantly improve the healing process and provide relief to patients. The tape’s unique properties offer pain relief, support, and enhanced proprioception, enabling patients to recover faster and return to their daily activities with confidence. However, it is essential for therapists to regularly assess the patient’s progress, adjust the tape application as needed, and complement the treatment with other appropriate modalities to ensure a successful recovery.
By following these treatment methods, individuals can effectively manage and recover from an abdominal strain. However, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. They may also provide additional recommendations such as physical therapy exercises or the use of supportive devices like abdominal binders to aid in the healing process. Ultimately, with proper care and patience, individuals can expect a full recovery from an abdominal strain.
Rest and recovery
Rest and recovery are crucial aspects of the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal strain. When an individual experiences an abdominal strain, it is essential to allow the injured area to rest and heal properly. Resting helps reduce inflammation and prevents further damage to the affected muscles. It is recommended to avoid any activities or exercises that may aggravate the strain, such as heavy lifting or intense physical exertion. By providing adequate rest, the body can focus on repairing the injured tissues and speeding up the recovery process.
In addition to rest, applying cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with abdominal strain. Cold therapy, such as an ice pack or a cold towel, can be applied for 15-20 minutes several times a day. This helps constrict the blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the injured area and minimizing swelling.
Cold therapy can also help numb the area, providing temporary pain relief. It is important to note that the cold compress should not be applied directly to the skin but should be wrapped in a thin cloth or towel to prevent frostbite.
While rest and cold therapy are effective for the initial treatment of abdominal strain, it is crucial to gradually reintroduce activity and exercise as the injury heals. Once the pain and inflammation have subsided, a gradual return to normal activities can help strengthen the abdominal muscles and prevent re-injury.
It is advised to start with gentle stretching and low-impact exercises, gradually increasing the intensity and duration over time. However, it is important to listen to the body and avoid pushing through any pain or discomfort. If the pain persists or worsens during the recovery process, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is an essential component in the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal strain. Abdominal strain, also known as a pulled abdominal muscle, occurs when the muscles in the abdomen are overstretched or torn. It is a common injury that can result from activities such as heavy lifting, sudden twisting movements, or sports-related activities. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of abdominal strain, helping to reduce pain, improve flexibility, and promote healing.
In the initial stages of physical therapy for abdominal strain, the therapist will focus on reducing pain and inflammation. This may involve the use of ice packs or other cold therapy techniques to reduce swelling and alleviate discomfort. The therapist may also recommend gentle stretching exercises to help improve flexibility and reduce muscle stiffness. These exercises will be carefully tailored to the individual’s specific needs and abilities, ensuring that they do not exacerbate the injury.
As the healing progresses, the physical therapist will gradually introduce more challenging exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles. These exercises may include core stabilization exercises, such as planks or abdominal crunches, which help to improve the overall stability and support of the abdominal muscles. The therapist will closely monitor the patient’s progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. They may also incorporate other modalities such as heat therapy or electrical stimulation to further promote healing and relieve pain.
In summary, physical therapy is a vital component in the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal strain. The therapist will initially focus on reducing pain and inflammation through techniques such as cold therapy and gentle stretching exercises. As the healing progresses, more challenging exercises will be introduced to strengthen the abdominal muscles and improve overall stability. Physical therapy not only helps to alleviate pain but also promotes healing and prevents future injuries.
Medication options
When it comes to the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal strain, medication options play a crucial role in providing relief and promoting healing. Abdominal strains are typically caused by overuse or sudden twisting movements, resulting in the stretching or tearing of the muscles in the abdomen. To effectively manage this condition, healthcare professionals often consider the use of medications alongside other treatment modalities.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed for abdominal strains. These medications help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the affected area. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for pain and swelling. Over-the-counter NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are often sufficient for mild to moderate pain relief. However, for more severe cases, prescription-strength NSAIDs like diclofenac or meloxicam may be recommended.
Muscle relaxants can also be prescribed to patients with abdominal strains to help relieve muscle spasms and reduce discomfort. These medications work by acting on the central nervous system, specifically targeting the muscles to promote relaxation. Commonly prescribed muscle relaxants include cyclobenzaprine and methocarbamol. It is important to note that muscle relaxants may cause drowsiness and dizziness, so it is advisable to avoid activities that require alertness until the effects of the medication are known.
In addition to NSAIDs and muscle relaxants, topical analgesics can also be used to alleviate pain associated with abdominal strains. These creams, gels, or patches contain ingredients such as menthol or capsaicin, which provide a cooling or heating sensation to the affected area. Topical analgesics work by numbing the painful area, providing temporary relief. They can be used alongside oral medications or as an alternative for individuals who prefer not to take oral medications. However, it is important to follow the instructions on the packaging and consult a healthcare professional before using topical analgesics to ensure they are safe and appropriate for the individual’s specific condition.
In conclusion
Diagnosing and finding the right treatment can speed up your recovery and ensure you retain your hard work to date. Choosing the right method to treat your abdominal strain is essential to get back as early as possible on the road to recovery.





Leave a Reply